The proliferation of AI-generated content has introduced a new challenge in discerning truth from falsehood. This guide provides a structured approach to identifying AI-fabricated news, equipping readers with practical tools and techniques to navigate the complexities of the digital landscape.
From analyzing text patterns and source reliability to evaluating visual elements and checking for plagiarism, this resource offers a comprehensive framework for evaluating the authenticity of online information. By understanding the capabilities and limitations of AI, readers can develop critical thinking skills crucial for combating the spread of misinformation.
Identifying AI-Generated Text Patterns
AI-generated text, while rapidly improving, often exhibits distinct characteristics that can be detected by discerning readers. Recognizing these patterns can help in identifying potentially fabricated or misleading information. By understanding the stylistic quirks and predictable structures often employed by AI language models, we can better evaluate the authenticity of online content.Identifying AI-generated text requires a keen eye for detail and a nuanced understanding of language patterns.
The underlying algorithms used to train these models can sometimes produce output that is formulaic, predictable, or grammatically awkward, even when seemingly coherent. Learning to spot these irregularities is a crucial skill in the digital age.
Examples of Text Characteristics Associated with AI-Generated Content
Understanding the stylistic nuances of AI-generated text is crucial for discerning its authenticity. These models often produce output that is repetitive, lacking in originality, and predictable in structure. Specific characteristics include overly formal or overly casual language, an unusual emphasis on certain s or phrases, and a lack of natural flow or conversational cadence.
- Repetitive Language: AI models may inadvertently repeat words or phrases that are not characteristic of human writing. This repetition can manifest in a variety of ways, such as using similar sentence structures or employing identical or near-identical word choices within close proximity.
- Unusual Sentence Structures: AI-generated text sometimes demonstrates unnatural or overly complex sentence structures. These might be grammatically correct but deviate significantly from the typical patterns of human language. The structures can seem formulaic or overly precise.
- Lack of Natural Flow: AI models can sometimes struggle with crafting a natural flow of ideas. This may result in abrupt shifts in tone, topic, or logic, creating a jarring or disjointed reading experience. The text may not have the natural progression of ideas one would expect in a human-written piece.
- Predictable Language Patterns: AI models are trained on massive datasets, which can result in predictable patterns in language use. This may manifest as a tendency to use certain phrases or s in a stereotypical manner.
Spotting Unusual Sentence Structures or Phrasing
Careful scrutiny of sentence structures can reveal potential AI authorship. Analyzing sentence length, complexity, and grammatical structure can highlight unusual patterns. The frequency of complex, compound sentences might be significantly higher or lower than in typical human writing.
Techniques to Identify Repetitive or Predictable Language Patterns
Employing a systematic approach to analyze the text can uncover repetitive language patterns. This involves looking for patterns in word choice, sentence structure, and overall stylistic elements. One can use tools to analyze word frequency and identify unusual or unexpected correlations.
Comparison of Human vs. AI Writing Styles
| Characteristic | Typical Human Writing | AI-Generated Writing |
|---|---|---|
| Sentence Structure | Varied, often incorporating complex and compound sentences with natural transitions. | Often repetitive, with a tendency toward simpler sentence structures or formulaic combinations. |
| Vocabulary | Rich and varied, employing nuanced word choices appropriate to the context. | Potentially limited vocabulary, with a reliance on frequently encountered terms. |
| Flow and Coherence | Natural flow of ideas, logical progression, and conversational tone. | Potentially disjointed flow, abrupt transitions, and lack of natural cadence. |
| Originality | Unique perspectives, insightful observations, and creative expressions. | Reliance on existing data, often lacking originality and showing predictable tendencies. |
Common Stylistic Inconsistencies in AI-Generated Text
AI-generated text can exhibit inconsistencies in tone, style, and vocabulary. These inconsistencies can arise from the model’s inability to fully understand and replicate the nuances of human language.
Examining Content Consistency and Sources
Evaluating the consistency and reliability of information is crucial in discerning AI-generated fake news. This involves scrutinizing not only the text itself but also the sources cited within the article. A lack of internal consistency or reliance on questionable sources are strong indicators of potential manipulation. Careful analysis of these elements can help differentiate between authentic and fabricated information.Identifying inconsistencies in the presented information is a key step in determining its validity.
This includes checking for logical fallacies, contradictions, and discrepancies in data presented. For instance, a sudden shift in tone or narrative within a single article may suggest an attempt to mislead or manipulate. Similarly, conflicting statements or information presented from different sources within the same article should raise a red flag.
Evaluating Content Consistency
Determining the consistency of information involves a multi-faceted approach. Examine the flow of the argument and ensure that each point logically follows the previous one. Look for factual inaccuracies, inconsistencies in dates, statistics, or locations, and discrepancies in the presentation of evidence. The absence of supporting evidence or the use of vague language can also point to potential fabrication.
Assessing Source Reliability and Trustworthiness
Assessing the reliability and trustworthiness of cited sources is paramount. Examine the credentials of the authors or organizations mentioned. Check if the source has a reputation for accuracy and impartiality. Look for signs of bias, whether political, economic, or personal. Consider the source’s potential motives and whether they might have a vested interest in the information presented.
Determining Source Currency and Relevance
Evaluating the currency and relevance of cited sources is essential. Look for dates of publication or updates to determine if the information is current and pertinent to the topic. Outdated information or references to events long past may indicate a deliberate attempt to mislead. Consider whether the source is still active and relevant to the specific topic being discussed.
For instance, a news article from 2010 on a contemporary political event would likely be outdated and irrelevant.
Identifying Fabricated or Manipulated Sources
Detecting fabricated or manipulated sources requires a keen eye for detail. Examine the URL of the website. Look for unusual or suspicious formatting, a lack of clear authorship, and absence of contact information. Check for established and reputable organizations or publications behind the source. Compare the cited sources with established and trusted news organizations.
Determining Plausibility and Accuracy
Determining the plausibility and accuracy of the information presented requires critical thinking. Consider the context of the information and its potential implications. Evaluate whether the claims made align with known facts and evidence. Use established knowledge to check the information against known facts. If a claim seems extraordinary or contradicts widely accepted knowledge, it warrants further investigation.
For example, a claim of a new scientific discovery without any peer-reviewed publications should raise suspicion. A claim that contradicts well-established scientific principles is highly improbable.
Analyzing Logical Fallacies and Biases
AI-generated fake news often relies on flawed reasoning and manipulative techniques to deceive readers. Understanding these tactics is crucial for discerning truth from falsehood. Identifying the biases embedded within the content, along with the logical fallacies used, significantly enhances one’s ability to critically evaluate information.Recognizing logical fallacies and biases in AI-generated text requires a careful examination of the information presented, including its sources and supporting evidence.
This process involves identifying patterns of flawed reasoning, emotional appeals, and unsubstantiated claims that are commonly used in such content.
Common Logical Fallacies in AI-Generated Fake News
Identifying common logical fallacies is key to evaluating the credibility of AI-generated fake news. These fallacies, while often subtly presented, can significantly mislead readers. A deeper understanding of these patterns helps in recognizing potential manipulation.
| Logical Fallacy | Description | Example (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| Appeal to Authority | Citing an unqualified or irrelevant authority figure. | A celebrity endorses a product, despite having no expertise in its field. |
| Bandwagon Fallacy | Claiming something is true because many people believe it. | “Everyone is buying this product, so it must be great.” |
| False Dilemma | Presenting only two options when more exist. | “You are either with us or against us.” |
| Straw Man | Misrepresenting an opponent’s argument to make it easier to refute. | Misrepresenting someone’s position to make it seem absurd. |
| Slippery Slope | Arguing that one action will inevitably lead to a series of negative consequences. | “If we allow this policy, it will lead to a complete collapse of society.” |
Identifying Biases in AI-Generated Content
AI models can inadvertently or intentionally incorporate biases from the data they are trained on. Identifying these biases is crucial for evaluating the information’s fairness and objectivity.
- Confirmation Bias: AI-generated content might focus heavily on information that confirms pre-existing beliefs, while ignoring contradictory evidence. Look for an absence of opposing viewpoints or sources.
- Gender Bias: AI models trained on biased data sets may perpetuate gender stereotypes or portray certain genders in a skewed manner.
- Racial Bias: Similarly, AI models can reflect racial stereotypes or inequalities present in the training data, leading to skewed portrayals of various racial groups.
Spotting Emotional Appeals and Unsubstantiated Claims
Emotional appeals, like fear-mongering or playing on patriotism, are often used to manipulate readers into accepting claims without proper scrutiny. Similarly, unsubstantiated claims lack supporting evidence.
- Emotional Appeals: AI-generated content may employ emotional language to evoke strong feelings, making readers more susceptible to accepting the presented information.
- Unsubstantiated Claims: Look for statements lacking concrete evidence or verifiable sources. Examine the reasoning and supporting data to identify unsubstantiated or exaggerated claims.
Recognizing Flawed Reasoning and Illogical Arguments
AI-generated content can contain illogical arguments and flawed reasoning. Understanding these patterns can help identify misinformation.
| Flawed Reasoning Type | Description | Example (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|
| Circular Reasoning | Supporting a statement with the statement itself. | “This is true because it says it is true.” |
| Hasty Generalization | Drawing conclusions based on insufficient evidence. | “Based on one bad experience, all restaurants in the city are terrible.” |
Evaluating Visual Elements and Multimedia

Visual elements, including images and videos, play a crucial role in disseminating information. However, these elements can be manipulated to create misleading or fabricated content. Critically evaluating visual elements is essential for discerning authenticity and avoiding the spread of false information. Sophisticated techniques for manipulating visuals are readily available, making it more challenging to identify genuine content.Assessing visual elements involves scrutinizing various aspects for inconsistencies, manipulations, and inaccuracies.
This includes examining the source of the media, looking for anomalies in image quality, and analyzing potential discrepancies between visuals and the accompanying text. Understanding these techniques helps in effectively identifying and avoiding AI-generated fake news.
Analyzing Image Quality and Resolution
Visual artifacts and inconsistencies in image quality can be indicative of manipulation. Poor resolution, pixelation, or unusual color distortions can suggest that an image has been altered or fabricated. For example, a high-resolution image of a historical event, inserted into a low-resolution news report, raises suspicion. Similarly, a photograph of a person with unusual lighting or shadows that don’t match the time of day, or a noticeable change in skin texture, might indicate image manipulation.
Analyzing the image’s metadata, such as the date and time it was taken, can also offer valuable clues.
Identifying Manipulation Techniques in Images and Videos
Several techniques are used to manipulate images and videos, making them appear authentic while concealing their fabricated nature. These techniques can include image splicing, where portions of different images are combined to create a new image, or using image editing software to alter colors, lighting, and details. Digital video manipulation, like altering or replacing footage, is another tactic.
In videos, inconsistencies in frame rate, shaky camera movements, or noticeable changes in background elements might indicate tampering.
Assessing Authenticity of Images and Videos
Evaluating the source of the visual content is critical. Reputable news organizations often have established verification procedures and practices. Checking the source of the visual against known information sources, like archives or other reliable reports, is essential. Examining the date and time of the image or video, especially if it relates to an event, can help in identifying potential inconsistencies.
Spotting Inconsistencies Between Visuals and Text
A crucial aspect of evaluating visual content is comparing it with the accompanying text. If the image depicts a scene different from what the text describes, or if the details in the image contradict the information in the text, it indicates potential manipulation. For instance, a news article claiming a large crowd at a protest, but the image shows a relatively small group, warrants further investigation.
Table of Visual Manipulation Techniques
| Manipulation Technique | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Image Splicing | Combining parts of different images. | A photo of a person in one location, spliced onto a background image of another location. |
| Color/Lighting Alteration | Modifying colors or lighting in an image. | A historical photo with altered lighting to make it appear more modern. |
| Object Removal/Addition | Removing or adding objects to an image. | Removing a person from a crowd photo, or adding an object to a scene. |
| Video Frame Rate/Speed Alteration | Altering the frame rate or speed of a video. | Slowing down or speeding up a video to make an event appear different. |
| Video Footage Replacement | Replacing video footage with fabricated content. | Using a different video clip to replace a segment in a video. |
Checking for Plagiarism and Originality
Identifying plagiarized or rehashed content is crucial in evaluating the authenticity of information, especially when dealing with AI-generated text. AI models often learn from existing text, potentially producing outputs that mimic the style and structure of original sources without attribution. This necessitates a proactive approach to verifying the originality of the content.
Methods for Detecting Plagiarism
Effective detection of plagiarism requires a multi-faceted approach, combining various techniques. Manual review, utilizing specialized tools, and understanding the context of the content are all essential steps in verifying the authenticity of the material.
- Manual Review: A meticulous review of the text for similarities in phrasing, sentence structure, and overall argumentation is a fundamental step. This involves a close reading of the text, paying attention to unique phrasing and identifying potential instances of verbatim copying or paraphrasing. It is important to consider the context of the content and the potential for unintentional similarity.
- Plagiarism Detection Tools: Several online tools are specifically designed to detect plagiarism. These tools compare the text to a vast database of existing content, flagging potential matches. However, these tools should be used judiciously, as false positives can occur. Some tools are more sophisticated than others, and their accuracy can vary depending on the database they utilize.
- Source Verification: Examining the sources cited by the text is critical. If the text is extensively drawing on specific sources without proper attribution, it raises a red flag. A comprehensive evaluation of the sources can reveal whether the content is original or a rehash of existing information.
Identifying AI-Generated Text Adaptations
AI models are trained on vast datasets of text. This training can lead to AI-generated text that mirrors existing sources in style, structure, or argumentation. Identifying these adaptations is crucial to evaluate the originality of the content.
- Analyzing Sentence Structure and Style: AI-generated text often exhibits certain patterns in sentence construction and stylistic choices. While these patterns can be subtle, observant readers can identify them by recognizing repetition of sentence structures or predictable transitions between ideas. By analyzing the stylistic elements, we can gain insights into the potential for AI involvement.
- Evaluating the Information Flow: The flow of information in the text should be carefully examined. If the text follows a predictable pattern or closely resembles the structure of other sources, this can suggest that it is a rehash of existing information or was generated by an AI model.
- Checking for Unnatural Fluency: While AI-generated text is often quite fluent, sometimes it exhibits unnatural patterns or inconsistencies in tone or register. A careful review can reveal these inconsistencies. This could include unexpected stylistic shifts, unnatural phrasing, or the repetition of certain s or phrases.
Analyzing Text for Originality and Authorship
Assessing the originality and authorship of a text is an important aspect of evaluating its credibility. By combining several techniques, we can gain a more complete understanding of the source and its potential for plagiarism.
- Checking for Consistency: Assess the overall consistency of the text. Inconsistencies in tone, style, or information can suggest that the text is a compilation of various sources or was produced by multiple authors.
- Evaluating Supporting Evidence: Examine the supporting evidence provided in the text. If the evidence is weak or lacks context, it could be a sign that the information is not original. The validity and strength of the evidence used to support the arguments in the text are important factors in evaluating its originality.
- Identifying Unique Perspectives: A truly original text often presents unique perspectives or insights. If the text fails to offer a fresh perspective, it might be a rehash of existing ideas. An original piece often has a fresh perspective, which can be a useful signal for detecting originality.
Utilizing Fact-Checking Resources
Verifying information’s accuracy is crucial in the age of readily available, yet often misleading, content. Fact-checking websites and organizations provide a valuable service by rigorously evaluating claims and sources. This process ensures that individuals can discern credible information from potentially fabricated or biased content, promoting informed decision-making.
Reputable Fact-Checking Websites and Organizations
Fact-checking organizations employ trained analysts and methodologies to assess the validity of claims. They scrutinize evidence, cross-reference information, and analyze the context surrounding statements. Their goal is to provide users with unbiased assessments of information. Recognizing these reputable organizations is essential for utilizing fact-checking resources effectively.
| Organization | Focus/Specialization | Reputation/Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| Snopes | Extensive database of urban legends, rumors, and misinformation | Well-known for its in-depth investigations and comprehensive approach. |
| PolitiFact | Focuses on political statements and claims | Employs a rating system to assess the truthfulness of statements. |
| FactCheck.org | Examines claims from political campaigns, public figures, and media outlets | Known for its rigorous standards and transparency in its methodology. |
| Reuters Fact Check | News agency providing fact-checks on various topics | Leverages a global network of journalists and experts. |
| AFP Fact Check | International news agency offering fact-checking services | Utilizes a global network of journalists to assess claims. |
Effective Use of Fact-Checking Tools
To utilize fact-checking tools effectively, one should approach claims with a critical eye and understand the methodologies employed by these organizations. Understanding the process involved in fact-checking enhances one’s ability to evaluate the credibility of information.
- Thorough Research: Before submitting a claim to a fact-checking website, carefully examine the context surrounding the information. Consider the source of the information and its potential biases. Providing a comprehensive background to the claim allows for a more accurate assessment.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Review the fact-checker’s analysis of the claim. Pay close attention to the evidence presented, and assess the reasoning used to arrive at the conclusion. Note any supporting or contradicting evidence. Fact-checking websites often present different perspectives to highlight the complexities of a claim.
- Critical Evaluation: Evaluate the accuracy and reliability of the sources cited by the fact-checker. Look for any inconsistencies or inaccuracies in the evidence. Scrutinize the fact-checker’s methodology to determine if it is appropriate and comprehensive.
- Contextual Understanding: Understanding the claim’s context is crucial. Fact-checking websites often provide insights into the historical background, motivations, and potential biases associated with the claim. Comprehending the historical context and motivations allows for a more holistic evaluation.
Verifying Claims and Sources
By employing a structured approach to verification, users can effectively evaluate the authenticity of claims and sources. This involves a careful consideration of the provided evidence and the methodologies used by fact-checkers.
- Identifying Claims: Carefully identify the specific claims or statements being made. Clearly articulate the claim’s subject and its assertion.
- Locating Sources: Seek out the original sources referenced by the fact-checking website. Evaluate the reliability and credibility of these sources. Verify the context in which the claim was made and if there is any surrounding information.
- Cross-Referencing Information: Cross-reference the fact-checker’s findings with other credible sources. This helps corroborate the information presented. Multiple sources, if they agree, often strengthen the validity of a fact-check.
- Assessing Biases: Identify potential biases in both the original source and the fact-checking organization. Consider whether the information presented might be influenced by personal or organizational perspectives.
Reliable Fact-Checking Organizations
Using these organizations, individuals can gain confidence in the accuracy of information they encounter. Their rigorous methodology and expertise provide a valuable resource for verifying claims.
- Snopes
- PolitiFact
- FactCheck.org
- Reuters Fact Check
- AFP Fact Check
Understanding AI Capabilities and Limitations
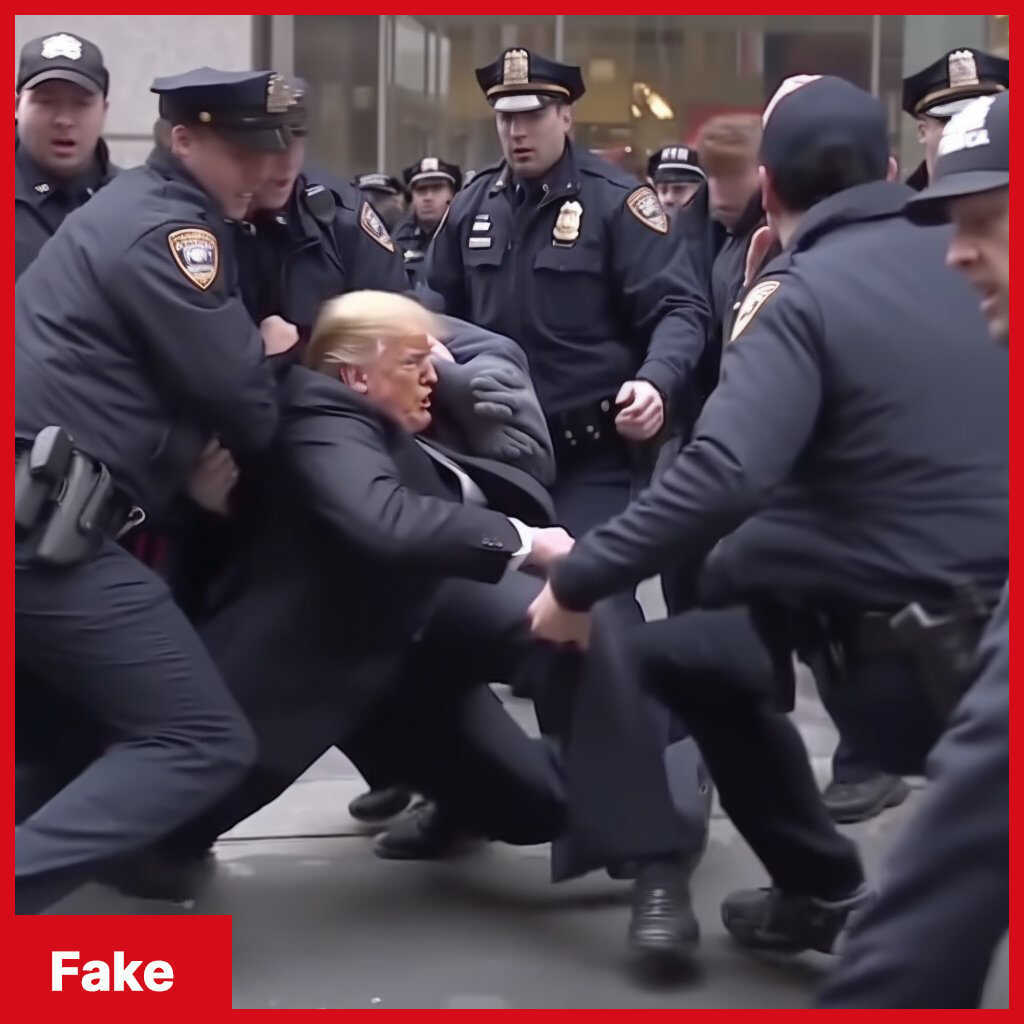

AI systems are rapidly evolving, demonstrating impressive capabilities in generating various forms of text and media. However, a crucial understanding of their limitations is essential for discerning authentic information from AI-fabricated content. This section explores the strengths and weaknesses of AI text and media generation, highlighting how these systems can produce realistic but ultimately flawed outputs.AI systems excel at mimicking human writing styles and generating coherent text on a wide range of topics.
They can synthesize information from vast datasets, allowing for the creation of articles, poems, scripts, and even code. Moreover, AI can generate realistic images, audio, and video, blurring the lines between human-created and machine-generated content.
AI Capabilities in Text and Media Generation
AI models, particularly large language models (LLMs), are trained on massive datasets of text and code. This training allows them to identify patterns and relationships in the data, enabling them to generate new text that mimics the style and structure of the training data. Furthermore, advancements in deep learning enable AI to generate various forms of media, including realistic images, videos, and even audio recordings.
These advancements make it increasingly challenging to distinguish AI-generated content from human-created content.
Realistic but Flawed Outputs
AI systems often produce outputs that appear remarkably human-like. This is due to their ability to capture nuances in language, style, and even tone. However, despite their impressive abilities, AI outputs frequently lack the depth, originality, and nuanced understanding that comes from human experience and critical thinking. This can manifest in the form of illogical conclusions, factual errors, or inconsistencies in the narrative.
For example, an AI might generate a convincing news article on a complex scientific topic, but fail to accurately represent the intricacies of the underlying research or the range of perspectives in the scientific community.
Limitations of Current AI Technology
Current AI technology faces limitations in generating complex and nuanced content. These systems often struggle with understanding context, particularly when faced with ambiguous or contradictory information. Moreover, their ability to create original and meaningful content remains constrained. The outputs are primarily based on statistical patterns identified in the training data, potentially leading to repetition, bias, or the perpetuation of harmful stereotypes.
The ability to understand the underlying logic and reasoning behind complex ideas remains a challenge for current AI systems.
Identifying AI-Generated Content
Identifying AI-generated content requires a careful examination of the text and media. While no single definitive method exists, certain patterns may suggest AI involvement. These include:
- Lack of Originality and Creativity: The content might repeat phrases or structures found in the training data, lacking the unique voice and perspective of a human author.
- Inconsistencies in Style and Tone: The writing style might abruptly change or exhibit inconsistencies in tone and vocabulary, indicating a lack of coherent authorship.
- Over-reliance on Specific Vocabulary: An excessive use of specific terminology, potentially without proper context or explanation, may indicate the content was generated by a system trained on a particular dataset.
Potential Biases and Errors
AI systems inherit biases present in their training data. These biases can manifest in the generated content, leading to unfair or inaccurate portrayals of individuals, groups, or ideas. Moreover, AI systems are susceptible to errors in their calculations, which can lead to factual inaccuracies and logical fallacies in the generated content.
- Bias in Language: AI systems may reproduce or even amplify biases present in the training data, leading to potentially discriminatory or unfair representations.
- Factual Errors: AI systems might misinterpret or misrepresent information, leading to factual inaccuracies in the generated text or media.
Epilogue

In conclusion, recognizing AI-generated fake news requires a multi-faceted approach. By understanding the unique characteristics of AI-produced content, evaluating sources, scrutinizing logic and visuals, and utilizing fact-checking resources, individuals can develop a robust toolkit for discerning truth from fabrication. This guide empowers readers to critically assess online information and contribute to a more informed digital environment.