Mastering the art of rephrasing is crucial for effective communication across various domains, from academic writing to business correspondence. This guide delves into the intricacies of rephrasing, exploring the fundamental principles and advanced techniques. It details how to enhance your writing through sentence and paragraph manipulation, and how AI tools can significantly streamline this process.
From identifying key sentence components to employing AI-powered rephrasing tools, this comprehensive resource provides practical examples and case studies. Learn how to maintain clarity, conciseness, and original meaning while adapting your writing for different audiences and purposes. Understanding the importance of avoiding plagiarism throughout the process is also emphasized.
Introduction to Rephrasing
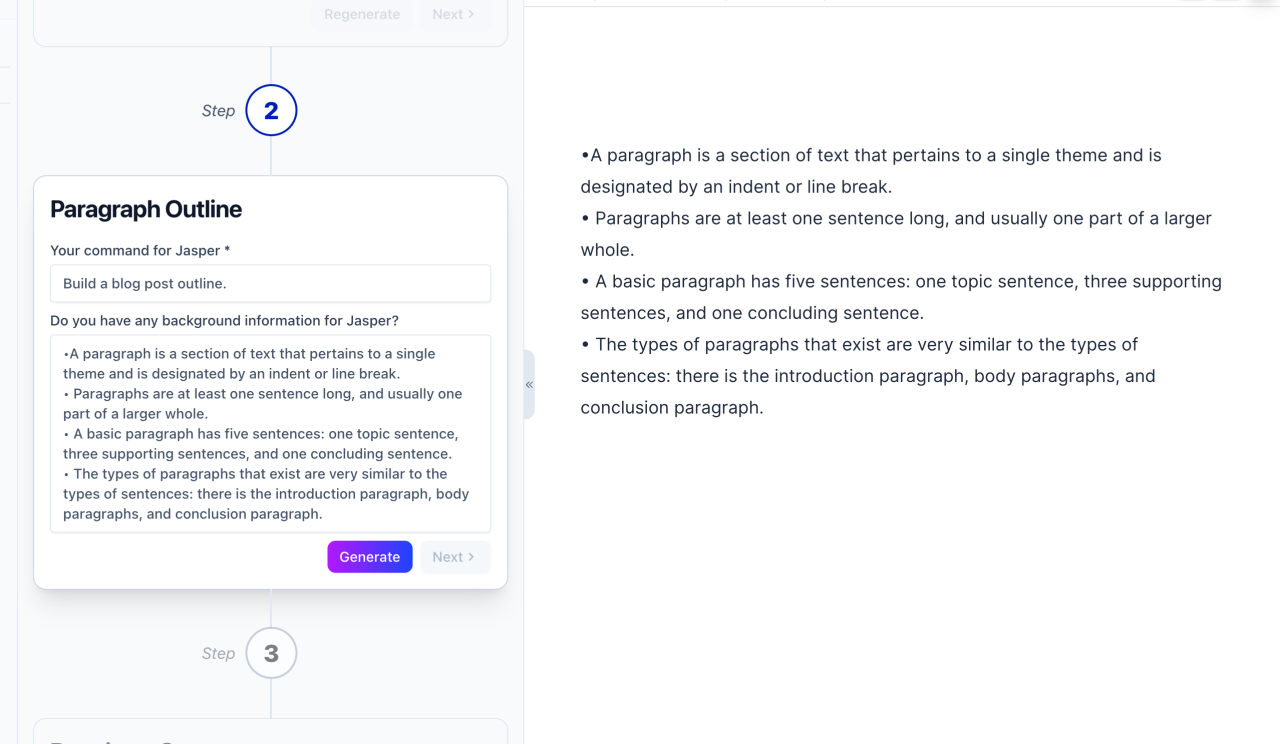
Rephrasing involves restating a sentence or paragraph in a different way, using synonyms, different sentence structures, or a more concise or elaborate style. It is a crucial skill across various communication fields, as it enhances clarity, conciseness, and impact. Effective rephrasing often leads to a more impactful and nuanced message.Rephrasing is not simply about finding a synonym. It’s about understanding the original meaning and conveying it in a way that better suits the specific context and audience.
This process can significantly enhance the readability and comprehension of any text, from academic research papers to creative fiction and business proposals.
Importance of Rephrasing
Rephrasing is essential in numerous contexts due to its ability to improve communication and impact. In academic writing, it allows for a more formal and sophisticated tone while avoiding plagiarism by presenting ideas in different words. In creative writing, it can lead to a more engaging and evocative style, allowing the author to convey emotions and imagery more powerfully.
Business communication benefits from rephrasing to ensure clarity and precision in conveying information, instructions, and decisions, promoting efficiency and minimizing misinterpretations.
Reasons for Rephrasing
Rephrasing is necessary for various reasons. Clarity and conciseness are paramount in most written communication. Rephrasing can help remove ambiguity and ensure the intended meaning is conveyed accurately. Adapting to different audiences is another critical aspect. A message aimed at experts might need to be rephrased to be understood by a wider audience.
Rephrasing also plays a key role in avoiding redundancy and repetition. By restating ideas in new ways, writers can maintain reader engagement and ensure the text flows smoothly. Finally, rephrasing allows for a more persuasive and compelling message, impacting the reader or listener more effectively.
Benefits of Rephrasing
The benefits of rephrasing are multifaceted and impactful. Improved clarity and conciseness make the message more easily understood and retained. Enhanced impact on the reader or listener can lead to greater engagement and a stronger overall impression. Rephrasing facilitates a more nuanced and sophisticated style of writing, suitable for academic and professional contexts. Furthermore, rephrasing can increase the persuasive power of a message, making it more effective in achieving its desired goal.
Lastly, rephrasing helps to avoid plagiarism by expressing ideas in unique ways while retaining the core meaning.
Rephrasing Techniques
Different methods exist for rephrasing sentences and paragraphs. A variety of techniques can help achieve the desired level of clarity and impact.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Using synonyms | Replacing words with their synonyms to alter the sentence’s tone and feel without changing the core meaning. |
| Changing sentence structure | Modifying the sentence’s grammatical structure (e.g., from active to passive voice) to alter the emphasis or flow. |
| Paraphrasing | Restating an entire passage in different words while retaining the original meaning. |
| Summarization | Condensing a longer passage into a shorter, more concise version, highlighting the main points. |
| Expanding | Elaborating on a concise passage to provide more detail and context. |
Identifying Sentence Structure
Understanding sentence structure is fundamental to effective communication. Sentences, the building blocks of paragraphs and narratives, convey meaning through their arrangement of components. By grasping the key elements and their relationships, we can better analyze and manipulate sentences for clarity and impact. This section delves into the core components of a sentence, the importance of their arrangement, and how to dissect various sentence structures.Sentence structure dictates how meaning is conveyed.
A well-structured sentence is clear, concise, and easily understood. Conversely, a poorly structured sentence can lead to ambiguity and confusion. Mastering sentence structure empowers us to articulate ideas with precision and impact.
Key Components of a Sentence
Sentences are composed of essential elements that contribute to the overall meaning. Identifying these components is the first step in understanding sentence structure. These key elements include the subject, the verb, and the object. The subject performs the action; the verb describes the action; and the object receives the action.
- The subject of a sentence is the noun or pronoun that performs the action. For example, in the sentence “The dog barked,” “dog” is the subject.
- The verb of a sentence expresses the action or state of being. In the sentence “The dog barked,” “barked” is the verb.
- The object of a sentence, if present, receives the action of the verb. In the sentence “The dog chased the cat,” “cat” is the object.
Significance of Sentence Structure
The arrangement of these components significantly impacts the meaning conveyed. A shift in the order can alter the emphasis and even the overall message. For instance, “The cat chased the mouse” and “The mouse was chased by the cat” convey the same information but place different emphasis on the actors in the event.
Impact on Clarity and Conciseness
The way a sentence is structured directly influences its clarity and conciseness. A well-structured sentence clearly communicates the intended message, while a poorly structured sentence can be confusing and difficult to follow. Concise sentences, often with clear subjects, verbs, and objects, are more effective in conveying meaning without unnecessary words.
Analyzing Different Sentence Structures
Various sentence structures exist, each with its own nuances and communicative purposes. Understanding these structures enables us to analyze and rephrase sentences for different effects.
| Sentence Structure | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Sentence | Consists of a single independent clause. | The sun rises in the east. |
| Compound Sentence | Combines two or more independent clauses. | The sun rises in the east, and the birds sing. |
| Complex Sentence | Contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. | Because the sun rises, the world wakes. |
| Compound-Complex Sentence | Combines two or more independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses. | Although the sun rises in the east, the birds sing, and the world wakes. |
Methods for Rephrasing Sentences

Rephrasing sentences and paragraphs is a crucial skill in communication, enabling you to express the same idea in various ways. This adaptability allows for clearer, more concise, and contextually appropriate expression. Mastering rephrasing techniques significantly enhances writing and speaking effectiveness.Rephrasing is not simply about finding synonyms; it involves a deeper understanding of sentence structure, purpose, and audience. This process can include altering the voice of a sentence, restructuring the grammatical elements, and choosing different words while maintaining the core meaning.
It is a dynamic approach to communication that fosters flexibility and precision in conveying information.
Rephrasing Simple Sentences
Simple sentences, typically consisting of a subject and a verb, offer straightforward opportunities for rephrasing. This often involves using different word choices without changing the core meaning. For example:
- Original: The cat sat on the mat.
- Rephrased 1: A feline perched atop a rug.
- Rephrased 2: On the mat, the cat rested.
These examples demonstrate how seemingly minor adjustments can yield varied expressions while maintaining the same fundamental concept.
Rephrasing Complex Sentences
Complex sentences, often including subordinate clauses, require a more nuanced approach to rephrasing. Here, the focus shifts to reorganizing clauses, changing the sentence structure, and altering the focus of the sentence while preserving the intended meaning. Consider this example:
- Original: Because the weather was dreadful, the picnic was postponed until next weekend.
- Rephrased: The picnic was rescheduled for next weekend due to the poor weather.
Notice how the rephrased sentence maintains the core meaning while using a different grammatical structure and vocabulary.
Methods for Rephrasing Passive Voice into Active Voice
Passive voice sentences often lack clarity and directness. Transforming them into active voice enhances the impact and conciseness of your writing.
- Identifying Passive Voice: A passive voice sentence typically places the recipient of the action at the beginning of the sentence. The subject receives the action, not performs it.
- Converting to Active Voice: To rephrase passive voice into active voice, identify the agent (the doer of the action) and place it at the beginning of the sentence as the subject.
- Examples:
- Passive: The report was written by John.
- Active: John wrote the report.
A systematic approach to identifying and correcting passive voice enhances clarity and impact.
Rephrasing Sentences Using Synonyms and Antonyms
Synonyms and antonyms provide a powerful tool for rephrasing sentences. Synonyms allow for replacement of words with similar meanings, while antonyms introduce contrasting ideas.
- Using Synonyms: Replacing words with their synonyms can add variety and richness to your writing. For example:
- Original: The child was happy.
- Rephrased: The child was joyful.
- Using Antonyms: Employing antonyms can create a contrast or highlight a specific aspect of a sentence. For example:
- Original: The event was successful.
- Rephrased: The event was unsuccessful.
This careful selection of words can significantly affect the tone and meaning of your writing.
Rephrasing Sentences for Different Purposes
Rephrasing for various purposes (e.g., formal, informal) requires considering the audience and context. Formal writing necessitates precise language and avoids colloquialisms.
- Formal Writing: Use precise and objective language, avoiding slang or informal expressions.
- Informal Writing: Use more conversational language, employing slang and colloquialisms appropriately.
Careful adaptation to the context and audience ensures clarity and appropriateness.
Rephrasing to Improve Clarity and Conciseness
Rephrasing can significantly improve clarity and conciseness by restructuring sentences, employing more direct language, and removing unnecessary words. For example, long-winded sentences can be simplified.
- Eliminating Redundancy: Identify and remove repetitive or unnecessary words.
- Using Active Voice: Replacing passive voice with active voice enhances clarity and conciseness.
A clear and concise style significantly enhances the impact of your writing.
Maintaining Original Meaning While Changing Phrasing
Maintaining the core meaning while changing the phrasing requires a deep understanding of the original text. Focus on the core idea and express it in different words and structures.
- Understanding the Core Idea: Identify the fundamental message of the sentence.
- Using Different Structures: Alter the grammatical structure without altering the core meaning.
This ensures that the revised expression effectively communicates the intended message.
Rephrasing Paragraphs

Rephrasing paragraphs, similar to rephrasing sentences, involves altering the wording while maintaining the core meaning. This process is crucial for adapting content to different audiences and contexts. It enhances clarity, conciseness, and engagement. Effective rephrasing allows writers to communicate complex ideas in a more accessible and impactful way.
Examples of Rephrasing Short Paragraphs
Rephrasing short paragraphs often involves simple word substitutions or sentence rearrangements. Consider the following example:Original Paragraph: “The project’s initial phase involved significant research and development. This stage was crucial for understanding the market and identifying potential challenges.”Rephrased Paragraph 1: “Extensive research and development formed the project’s initial phase. This crucial stage facilitated market understanding and the identification of potential obstacles.”Rephrased Paragraph 2: “To properly understand the market and anticipate potential hurdles, the project’s initial phase focused on research and development.”These examples demonstrate how the core meaning remains consistent while the phrasing is altered.
Elaboration on Rephrasing Longer Paragraphs
Rephrasing longer paragraphs necessitates a more comprehensive approach. Beyond simple word swaps, it often requires restructuring sentences, reordering paragraphs, or even changing the overall structure of the argument. A deeper understanding of the original paragraph’s core message and supporting details is essential.
Maintaining the Overall Meaning of the Paragraph
Maintaining the original meaning is paramount. Any rephrasing should not introduce inaccuracies or alter the intended message. Carefully consider the original author’s intent and ensure the rephrased version conveys the same information. This involves understanding the relationships between ideas and how they contribute to the overall argument.
Techniques for Rephrasing Paragraphs to Fit Different Contexts
Different contexts demand different approaches to rephrasing. For instance, a technical report might require precise and formal language, while a blog post could benefit from a more conversational style. The rephrased content should seamlessly integrate with the surrounding text, avoiding abrupt shifts in tone or style.
Strategies for Rephrasing Paragraphs for a Target Audience
Understanding the target audience is key. If the audience is highly technical, the rephrased paragraph might require more detailed explanations. Conversely, for a general audience, the language should be simpler and more accessible. Consider the audience’s existing knowledge and vocabulary when crafting the rephrased version.
Comparison of Rephrasing Methods
| Rephrasing Method | Formal Style | Informal Style |
|---|---|---|
| Word Substitution | Suitable for maintaining formality, but may require careful selection of synonyms | Useful for creating a conversational tone, but avoid colloquialisms |
| Sentence Rearrangement | Effective for improving clarity and flow | Can create a more engaging reading experience |
| Paragraph Structure Adjustment | Essential for adapting the structure to a formal tone | May involve changing the flow to fit a conversational style |
| Tone Adjustment | Maintaining a professional tone is crucial | Adapting to the target audience’s preferred tone is necessary |
This table highlights the varying approaches to rephrasing paragraphs, depending on the desired style and audience.
AI Tools for Rephrasing
AI-powered tools are increasingly valuable for rephrasing text, offering a range of advantages over manual methods. These tools can significantly expedite the process, producing multiple variations of a sentence or paragraph with varying degrees of formality and style. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of these tools is crucial for effective and responsible use.Rephrasing tools leverage natural language processing (NLP) techniques to analyze the structure and meaning of text.
This analysis allows them to identify synonyms, rearrange sentence structures, and generate alternative phrasing options. The goal is to maintain the original meaning while presenting it in a new and often more concise or nuanced way.
Potential AI Tools
Several AI-powered tools can assist with rephrasing text. Their capabilities vary significantly, impacting the quality and suitability of the output for specific purposes. The selection of an appropriate tool depends on the desired outcome and the specific characteristics of the text being rephrased.
- Paraphrasing Tools: Numerous online tools are specifically designed for paraphrasing. These tools often employ various NLP techniques to generate alternative phrasing, potentially altering sentence structure and word choice. Examples include QuillBot, ParaphraseTool, and others. These tools typically focus on rephrasing individual sentences or short paragraphs, with varying degrees of success in preserving the original meaning and tone.
- Language Translation Services: While primarily intended for translating between languages, advanced translation services often incorporate rephrasing capabilities. These services can be valuable for adapting text for different audiences or contexts. For example, Google Translate, DeepL, and similar platforms sometimes offer rephrased versions of translated text. Their rephrasing abilities may not be as robust as dedicated paraphrasing tools, but they can still provide useful alternatives.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Sophisticated LLMs like those used in chatbots and writing assistants can perform complex rephrasing tasks, including adapting the tone and style of the original text. These tools can generate entire paragraphs or even articles with new phrasing while maintaining the original meaning, although they might occasionally introduce inaccuracies or unintended shifts in meaning. Examples include Kami and similar tools.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AI Rephrasing
AI tools offer significant advantages for rephrasing, such as speed and scalability. These tools can quickly generate multiple variations, enabling users to explore different ways of expressing an idea. However, these advantages are accompanied by potential drawbacks.
- Advantages: AI tools significantly reduce the time required for rephrasing, enabling writers to explore various options efficiently. They can produce numerous variations of a sentence or paragraph, helping writers discover alternative ways to express themselves. The speed and scale of AI-driven rephrasing are particularly beneficial for large volumes of text or repetitive tasks.
- Disadvantages: AI tools may not always accurately capture the nuances of the original meaning, potentially altering the intended message. Some tools might introduce inaccuracies or even generate nonsensical or inappropriate phrasing. The quality of the output can vary significantly depending on the tool and the complexity of the text being rephrased. There is also a need to critically evaluate the output generated by AI tools.
Evaluating AI Rephrased Text
A crucial aspect of using AI tools for rephrasing is evaluating the output. Users should not blindly accept the AI’s suggestions but should critically assess the accuracy and appropriateness of the generated text. This step involves comparing the rephrased text with the original, considering the context and intended audience, and ensuring the meaning and tone remain consistent.
- Accuracy Check: Verify that the rephrased text accurately reflects the original meaning. Look for instances where the meaning might have been altered or lost in translation.
- Contextual Analysis: Consider the specific context in which the text will be used. Ensure the rephrased text is appropriate for the intended audience and purpose.
- Tone and Style Evaluation: Evaluate if the rephrased text maintains the original tone and style or if it introduces unintended changes.
Tool Evaluation Table
The effectiveness of different rephrasing tools varies. The following table summarizes the strengths and weaknesses of several popular tools. This table is intended as a starting point for comparison and should not be considered exhaustive.
| Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
| QuillBot | Wide range of paraphrasing options, good for basic rephrasing tasks. | May occasionally alter the original meaning, sometimes generating less sophisticated phrasing. |
| ParaphraseTool | Reliable for generating alternative phrasing, often maintaining the original meaning. | May struggle with complex sentence structures or nuanced text. |
| Google Translate | Free and readily available, useful for quick rephrasing and translation. | Rephrasing capabilities are less advanced than dedicated paraphrasing tools. |
Best Practices for Rephrasing
Rephrasing sentences and paragraphs effectively involves more than just substituting words. It necessitates a careful consideration of the original intent, context, and the desired impact. A successful rephrasing maintains clarity, accuracy, and the essence of the original message. This section delves into the key principles for achieving effective and meaningful rephrasing.Effective rephrasing hinges on understanding the nuanced context surrounding the text.
This context includes the intended audience, the overall purpose of the communication, and the specific situation in which the text will be used. A rephrased sentence must accurately reflect the original meaning within this broader context.
Maintaining Original Intent
Understanding and preserving the original meaning is paramount in any rephrasing exercise. The goal is not to simply change words, but to convey the same message with different phrasing. This requires a deep understanding of the original author’s perspective and the intended effect on the reader. A simple word substitution might alter the tone or emphasis, potentially leading to misinterpretation.
Carefully consider the nuances of the original message and strive to replicate them in the rephrased version.
Contextual Considerations
Context is the bedrock of effective rephrasing. Consider the audience, purpose, and situation surrounding the text. A rephrased sentence used in a formal business report will differ significantly from one used in a casual conversation. Maintaining the appropriate context ensures the rephrased text is understood and accepted within its intended environment. The style and tone must be adjusted to align with the situation.
For example, a complex scientific concept might need simplification for a general audience without sacrificing its core meaning.
Guidelines for Effective Rephrasing
Rephrasing should strive for clarity, conciseness, and accuracy. Use clear and concise language that avoids ambiguity. Ensure the rephrased text conveys the same information as the original, without altering the intended meaning. Avoid overly complex or jargon-filled language that might confuse the reader. The key is to find a balance between simplicity and precision.
Impact of Tone on Rephrasing
Tone significantly influences how a message is perceived. A formal tone is appropriate for academic writing, while a more casual tone might be suitable for informal communication. Rephrasing should maintain the original tone or adapt it appropriately for the new context. For instance, a critical statement might be rephrased to sound more constructive without losing its core message.
Importance of Accuracy in Rephrasing
Accuracy is crucial. A rephrased sentence must accurately reflect the original meaning. Avoid unintentional misinterpretations or distortions of the original message. The rephrased text should not introduce new ideas or change the overall meaning. Verify that the rephrased text accurately represents the original intent.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Changing the meaning: This is the most significant pitfall. The rephrased text must convey the same meaning as the original. Any alteration in the core message can lead to miscommunication.
- Using overly complex language: Simplicity and clarity are key. Avoid using jargon or overly technical terms that might confuse the reader. Instead, use straightforward language to ensure the intended meaning is clear.
- Ignoring the context: Context significantly influences how a message is interpreted. Failure to consider the context can lead to misinterpretations and ineffective communication. Adapt the rephrased text to fit the specific context and audience.
- Losing the original tone: The tone of the original text should be considered. Maintaining the original tone or adapting it appropriately for the new context is essential. A shift in tone might not be suitable for the situation and could lead to a misunderstanding.
Examples and Case Studies
Rephrasing techniques, when applied correctly, can significantly enhance communication clarity and impact. This section provides practical examples and case studies to illustrate how rephrasing can be used effectively in various contexts, while emphasizing the importance of maintaining the original meaning. Understanding these examples will provide a strong foundation for implementing rephrasing strategies in your own communication.
Rephrased Sentence Examples
Rephrasing a sentence often involves changing the wording while preserving the core message. Here are a few examples:
- Original Sentence: “The project was completed on time and within budget.”
Rephrased Sentence: “We successfully delivered the project, meeting all deadlines and staying within the allocated resources.” - Original Sentence: “I am not able to attend the meeting.”
Rephrased Sentence: “Unfortunately, I will be unable to attend the meeting today.” - Original Sentence: “The results of the survey were not favorable.”
Rephrased Sentence: “The survey findings did not reflect the anticipated outcome.”
Rephrased Paragraph Examples
Rephrasing a paragraph involves altering the phrasing and sentence structure of an entire passage. This allows for a more concise, nuanced, or targeted delivery of the message.
- Original Paragraph: “The new software update has resolved many of the previous issues users experienced. The developers have implemented several fixes and optimizations to the application. These improvements are expected to enhance the overall user experience.”
Rephrased Paragraph: “The newly released software update addresses many of the previously reported user issues. Improvements in the application’s functionality and performance should lead to a more satisfactory user experience.”
Case Studies of Rephrasing
Successful business communications often rely on effective rephrasing. Consider a case study of a marketing team struggling to convey a new product feature to potential customers. Initial marketing materials used complex technical language, leading to confusion and low engagement. By rephrasing the descriptions into simpler, more accessible language, the team saw a significant increase in customer interest and conversions.
This demonstrates the practical application of rephrasing to achieve specific communication goals.
Rephrasing Across Different Fields
The ability to rephrase effectively is crucial across various fields. The following table illustrates how rephrasing can adapt language to different contexts:
| Field | Original Text | Rephrased Text |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Writing | “The system will automatically adjust based on input parameters.” | “The system dynamically adapts to the provided input values.” |
| Legal | “The defendant was found to be liable.” | “The court determined the defendant to be responsible.” |
| Journalism | “The study found a correlation between smoking and lung cancer.” | “Research suggests a link between smoking and lung cancer development.” |
Maintaining Original Meaning
A key aspect of rephrasing is preserving the original meaning. Rephrasing should not alter the core message or introduce inaccuracies. Using synonyms and different sentence structures is permissible, but the overall meaning must remain consistent. This is vital for clarity and avoids miscommunication.
Benefits of Rephrasing for Communication
Rephrasing enhances communication in numerous ways. It allows for more concise expression, making the message easier to understand and absorb. It also allows for more targeted delivery, enabling the message to resonate more deeply with the intended audience.
Practical Applications of Rephrasing
Rephrasing is applicable in many daily scenarios. Consider rephrasing instructions to a colleague to ensure they understand the steps clearly. Or, consider rephrasing a complex email to make it more accessible to a wider audience. These examples demonstrate the widespread usefulness of this technique.
Rephrasing for Specific Purposes

Rephrasing is not a one-size-fits-all process. The effectiveness of a rephrased sentence or paragraph hinges on understanding the intended audience and purpose. This section delves into tailored rephrasing techniques, considering various communication contexts. Choosing the right words and structure is crucial for conveying the intended message clearly and effectively to a specific audience and for a particular purpose.Rephrasing for specific purposes requires a keen awareness of the nuances of language and how different word choices and sentence structures can affect the impact of the message.
This involves not just replacing words but also considering the overall tone, style, and register of the text.
Rephrasing for Different Audiences
Understanding the audience’s background, knowledge level, and expectations is fundamental to effective rephrasing. Adapting language for a technical audience differs significantly from adapting it for a general audience.
- For a technical audience, precise terminology and unambiguous phrasing are essential. Complex concepts should be broken down into simpler, more manageable components. Technical jargon, if necessary, should be clearly defined or explained. For example, instead of saying “The algorithm optimizes resource allocation,” one might say “The program efficiently manages available resources to maximize output.”
- For a general audience, the language should be accessible and engaging. Avoid technical terms and instead use simpler, more evocative language. The emphasis should be on clarity and conciseness. For example, rather than “The system underwent rigorous stress testing,” one could say “The system was put through extensive tests to ensure its stability.”
Rephrasing for Different Purposes
The purpose of the communication significantly influences the approach to rephrasing. Different purposes call for different tones and structures.
- Persuasion requires a carefully crafted message that appeals to the audience’s emotions and logic. Rephrasing should emphasize the benefits and advantages of the proposed idea or action. For example, instead of saying “This policy will reduce costs,” one might say “Implementing this policy will significantly lower operational expenses and improve profitability.”
- Instruction focuses on clarity and ease of understanding. Rephrasing in this context should focus on breaking down complex instructions into smaller, manageable steps. Use simple, direct language and avoid jargon. For example, instead of “Utilize the advanced feature set,” one might say “Follow these steps to access the enhanced functionalities.”
Rephrasing Techniques for Specific Writing Styles
The table below illustrates how rephrasing techniques can be tailored to different writing styles:
| Writing Style | Rephrasing Technique | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Formal | Use precise vocabulary, avoid contractions, maintain a respectful tone. | Instead of “It’s a good idea,” say “This approach is considered advantageous.” |
| Informal | Employ contractions, use conversational language, maintain a friendly tone. | Instead of “The report indicates a positive trend,” say “The report shows things are looking up.” |
| Descriptive | Use vivid language, focus on sensory details, create a clear picture in the reader’s mind. | Instead of “The house was large,” say “The sprawling Victorian mansion commanded the entire block.” |
Rephrasing in Presentations and Speeches
In presentations and speeches, rephrasing plays a critical role in maintaining audience engagement and ensuring clarity. Rephrasing can be used to avoid redundancy, to make complex ideas accessible, and to adjust the language to the particular needs of the audience. Effective rephrasing in this context requires careful consideration of the specific needs of the presentation.
Rephrasing in Marketing Materials
Rephrasing in marketing materials is crucial for capturing the attention of the target audience. Marketing copy should be concise, engaging, and persuasive. Effective rephrasing in this context should emphasize the unique selling points of a product or service. By using evocative language and highlighting benefits, rephrased copy can increase engagement and conversions.
Avoiding Plagiarism During Rephrasing
Rephrasing text effectively requires a keen understanding of intellectual property rights and the ethical considerations surrounding using others’ work. Accurate rephrasing goes beyond simply changing words; it demands a comprehensive understanding of the original content and the ability to convey its meaning in your own words. This section delves into the crucial aspects of avoiding plagiarism while rephrasing sentences and paragraphs.Plagiarism, in its various forms, can have serious consequences, ranging from academic penalties to legal repercussions.
Therefore, meticulous attention to detail and a strong understanding of ethical academic practices are essential. This section provides a detailed framework for effectively rephrasing text without committing plagiarism.
Importance of Accurate Paraphrasing
Maintaining the original meaning while expressing it in your own style is crucial. Simply swapping words or altering sentence structure without grasping the core idea is insufficient. Accurate rephrasing ensures that you demonstrate understanding of the source material, not just a superficial manipulation of words. This is vital in academic and professional settings, where originality and intellectual integrity are paramount.
Techniques for Paraphrasing Accurately
Understanding the nuances of the source material is paramount. Engage with the text deeply, considering the author’s intent and the overall message. This involves more than simply reading the text; it necessitates actively engaging with the concepts presented.
- Break down complex sentences into simpler ones. Identify the key arguments and supporting details. Rephrasing each element separately allows for a more comprehensive understanding and subsequent accurate expression.
- Use synonyms and different sentence structures. This is a fundamental aspect of rephrasing. Seek out synonyms for key words and phrases without losing the original meaning. Also, experiment with alternative sentence structures to ensure a unique and original expression.
- Focus on the underlying ideas rather than the specific wording. Identify the core arguments and supporting details, and then express them in your own words, ensuring the meaning remains consistent.
Strategies to Avoid Unintentional Plagiarism
Unintentional plagiarism can occur even with the best intentions. Developing strategies to mitigate this risk is essential. This requires careful attention to detail and a clear understanding of what constitutes plagiarism.
- Actively engage with the source material by taking notes and summarizing the key points in your own words. This active engagement helps to ensure you fully understand the source’s content and to express it independently.
- Consult multiple sources on the same topic to broaden your understanding. Comparison across different perspectives allows for a deeper comprehension and expression of the topic in your own words. This approach prevents over-reliance on a single source and fosters a more holistic understanding.
- Re-write the content in your own words several times. This process helps to ensure the text is completely original, and helps avoid unintentional plagiarism by reducing reliance on the original wording.
Citation and Attribution
Proper citation and attribution are crucial for academic integrity. They acknowledge the original source and prevent plagiarism. A properly cited source demonstrates intellectual honesty and respect for the work of others.
- Use citation styles consistently. This includes adhering to a specific style guide (e.g., MLA, APA) to ensure accuracy and consistency in referencing sources.
- Quote directly only when necessary. Summarize and paraphrase whenever possible. Direct quotations should be used sparingly and only when essential to maintain the exact meaning of the original author’s words.
- Always include a complete citation for every source used, listing the author, title, publication date, and other relevant information as per the citation style chosen.
Examples of Plagiarism and How to Avoid Them
Plagiarism can take various forms. Recognizing these forms and understanding how to avoid them is crucial. Careful examination of examples of plagiarism and alternative approaches to presenting the information is necessary.
| Plagiarism Example | How to Avoid It |
|---|---|
| Directly copying a sentence or paragraph from a source without quotation marks and citation. | Quote the sentence/paragraph accurately and cite the source appropriately. |
| Paraphrasing a source but retaining the sentence structure and vocabulary. | Use different sentence structures and vocabulary to express the meaning in your own words. |
| Failing to cite a source when paraphrasing. | Always cite the source, whether quoting or paraphrasing. |
Guidelines for Correctly Referencing Sources
Following specific guidelines for referencing sources ensures academic integrity and avoids plagiarism.
- Use a consistent citation style (e.g., MLA, APA, Chicago). This ensures uniformity and clarity in your references.
- Provide complete and accurate information for each source. This includes author, title, publication date, and other necessary details.
- Consult the appropriate style guide for specific requirements. This is essential to ensure accuracy and adherence to academic standards.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, rephrasing is a multifaceted skill applicable to various writing contexts. This guide has illuminated the methods and strategies for rephrasing sentences and paragraphs effectively. By utilizing AI tools responsibly and adhering to best practices, you can enhance your writing, communicate with precision, and avoid plagiarism. The examples and case studies will equip you with the tools and knowledge to confidently apply these techniques in your own work.