Unlocking the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) often hinges on understanding Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). This guide demystifies the world of APIs, providing a clear roadmap for navigating the complexities of interacting with AI services. From fundamental concepts to practical applications and advanced considerations, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to effectively leverage AI APIs for your projects.
This comprehensive guide explores the essentials of APIs, covering various aspects, including different types, documentation, crucial concepts, and practical applications. We’ll delve into working with AI APIs, troubleshooting common issues, and safeguarding your interactions with best security practices. This knowledge will be invaluable for developers and anyone seeking to integrate AI into their work.
Introduction to APIs
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are the crucial intermediaries that enable different software systems to communicate and share data seamlessly. Imagine them as translators, allowing diverse programs to understand and interact with each other, even if they were built using different languages or technologies. AI services rely heavily on APIs to expose their functionalities to external applications, making their capabilities accessible and usable.APIs act as a well-defined set of rules and protocols, dictating how software components should interact.
This structured approach ensures that communication is standardized and reliable, facilitating the development of complex applications and integrations. This standardization is essential in the rapidly evolving landscape of AI-powered applications.
Different Types of APIs
APIs come in various forms, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right API for a specific task. RESTful APIs are exceptionally popular for their simplicity and efficiency. They utilize HTTP methods (like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to interact with resources, often represented as URLs. These APIs typically use JSON or XML for data exchange.
SOAP APIs, on the other hand, are more complex, employing XML as the primary data format and relying on a more rigid structure, offering a higher degree of control over the exchange process. Choosing the appropriate API type hinges on the specific requirements of the AI service and the application consuming it.
Key Components of an API
APIs have several fundamental components that define their functionality. These components are essential for developers to understand and utilize the API effectively. The following table provides a summary of these key components.
| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoints | Specific URLs that represent resources within the API. These URLs are the entry points for interacting with the API. | /users, /products, /orders |
| Methods | HTTP verbs (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) that specify the operation to be performed on a particular endpoint. | GET to retrieve data, POST to create new data |
| Parameters | Data provided to the API to refine or customize the request. These parameters can be included in the URL or in the request body. | Filters, sorting criteria, pagination information. |
| Responses | The data returned by the API in response to a request. These responses typically include status codes, headers, and a payload of data. | JSON or XML format containing user information, status codes (e.g., 200 OK, 404 Not Found). |
Understanding API Documentation

API documentation serves as the crucial guide for developers interacting with an API. It provides a comprehensive overview of the available functionalities, outlining how to utilize them effectively and efficiently. A well-structured and clear API documentation significantly reduces the learning curve for developers, enabling them to integrate the API into their applications quickly and accurately.Effective API documentation facilitates seamless integration and avoids potential errors during development.
This comprehensive approach ensures a smooth experience for both API providers and consumers.
Structured Format for Effective API Documentation
Well-structured API documentation is critical for user comprehension. It should clearly delineate the available endpoints, request formats, and response structures. The structure should be organized logically, allowing developers to quickly locate the specific information they need. This logical organization reduces confusion and improves the overall developer experience.
Navigating and Interpreting API Documentation
Navigating API documentation requires a clear understanding of the structure and content organization. Developers should familiarize themselves with the table of contents, search functionality, and other navigation aids. Careful reading of the documentation, paying attention to details such as parameters, authentication methods, and error codes, is crucial. This allows for an efficient understanding of the API’s capabilities and limitations.
Crucial Elements in API Documentation
Several key elements are essential in API documentation. Endpoints define the specific resources available through the API. Understanding request and response formats is vital for creating accurate requests and interpreting the returned data. Authentication methods, such as API keys or OAuth, are necessary for securing access to the API. These elements provide a complete picture of how to use the API.
Using Examples and Code Snippets
Examples and code snippets are invaluable tools within API documentation. They illustrate how to utilize the API in real-world scenarios. Developers can copy and paste the code, modify it to suit their needs, and quickly integrate the API into their applications. Code snippets demonstrate practical usage and facilitate a faster learning curve.
Comparing Presentation Formats
| Presentation Format | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text-based | Information presented in a sequential format, often using markdown or plain text. | Simple to read, can be easily generated and maintained. | Can be difficult to visualize complex relationships or data structures. |
| Interactive Tools | Tools like online sandboxes or API explorers allowing real-time testing and visualization. | Provides a dynamic way to interact with the API and visualize data, enabling faster understanding. | Requires a functional internet connection and may not cover all aspects of the API. |
| Graphical Representations | Diagrams or flowcharts visualizing API interactions and data flows. | Provides a visual understanding of the API structure and functionality. | Can become complex for intricate APIs and may not be as detailed as text-based documentation. |
API documentation presentation formats play a significant role in the developer experience. The chosen format should align with the complexity of the API and the needs of the target audience. Choosing the right format can streamline the development process and facilitate easier API integration.
Essential API Concepts
APIs are fundamental to modern applications, enabling seamless communication between different systems. Understanding the core concepts of API interactions is crucial for developers to effectively design and utilize these services. This section delves into the key components of API interactions, including requests, responses, data formats, authentication, and error handling.The core of any API interaction is the exchange of data between a client (the application using the API) and a server (the application providing the API).
This exchange is structured, with specific rules and protocols for the format and content of the communication.
Request and Response
API interactions are fundamentally based on the client making a request to the server and the server sending a response. The request Artikels the desired action, and the response conveys the result of that action. The request specifies what the client wants, and the response delivers the result, including data or status information.
Request Methods
Different request methods dictate the type of operation the client wants to perform. These methods are part of the HTTP protocol, which defines the rules for communication over the internet.
- GET: This method retrieves data from the server. It is typically used for reading resources. For example, retrieving a list of products or a specific product details. The request typically does not modify the server’s data.
- POST: This method sends data to the server for processing, often creating a new resource. A typical example would be submitting a new user registration form or uploading a file.
- PUT: This method updates an existing resource on the server. It’s often used to modify data associated with a specific resource, such as updating a user’s profile.
- DELETE: This method removes a resource from the server. It’s used to delete a specific resource, such as a user account or a product.
Data Formats
Different formats are used for the data exchanged in API interactions.
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): This is a lightweight format that is human-readable and widely used in modern APIs. It is based on key-value pairs and is easy to parse and interpret. JSON is commonly used for transferring data between web applications and servers.
- XML (Extensible Markup Language): This format uses tags to define data elements. While less popular than JSON for modern APIs, XML is still used in certain contexts, particularly in older systems or when complex data structures are needed.
Authentication
Security is paramount in API design. Authentication mechanisms ensure only authorized clients can access API resources.
- API Keys: A unique identifier assigned to a client, allowing the server to identify the client making the request. It’s a simple method for basic authentication.
- OAuth: This is an authorization framework that allows a third-party application to access a user’s data on another service. It provides a more secure and user-centric approach to authentication, as the client does not directly store user credentials.
Error Handling
Error handling is critical for robust API design. It ensures that clients receive informative messages about any issues encountered during the interaction.
- APIs use HTTP status codes to indicate the outcome of a request. Different codes signify different conditions, ranging from successful completion to errors.
HTTP Status Codes
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | OK (Request was successful) |
| 400 | Bad Request (The request was invalid) |
| 401 | Unauthorized (Authentication failed) |
| 404 | Not Found (The resource requested does not exist) |
| 500 | Internal Server Error (An error occurred on the server) |
Working with AI APIs
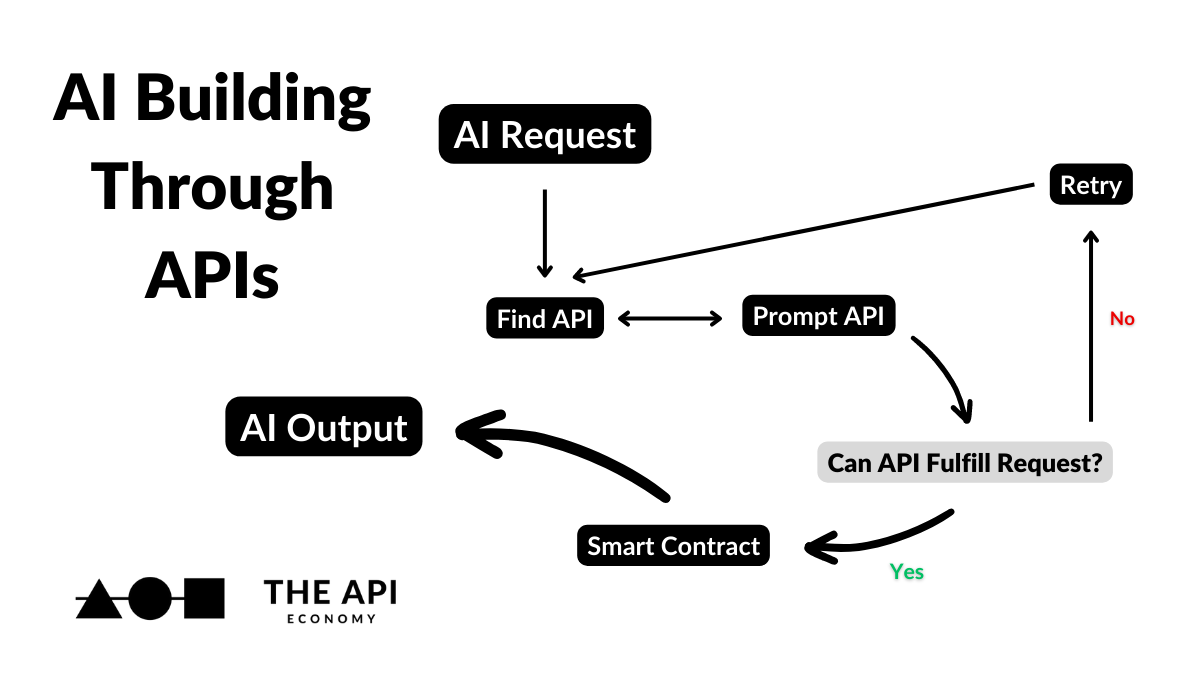
Leveraging AI APIs effectively necessitates a nuanced understanding of their specific requirements. This involves recognizing the distinct input and output formats expected by various AI models, and understanding how to structure API calls for diverse AI tasks. Furthermore, choosing the appropriate libraries for interacting with the API is crucial for streamlining the development process.
Input and Output Formats
AI models, irrespective of the task, require specific input formats. Understanding these formats is essential for successful interaction with the API. Similarly, the output format of the AI model needs to be interpreted correctly. Misinterpreting the data types or structures can lead to erroneous results. For instance, an image recognition API might expect images in a specific format (e.g., JPEG, PNG) and size, while a natural language processing API might require text input in a particular structure or encoding.
Output formats can vary from structured JSON or XML to more complex formats tailored for specific applications.
Making API Calls for Various AI Tasks
The process of making API calls for different AI tasks follows a standardized procedure. Generally, this involves constructing a request that includes the necessary input data and parameters, and sending this request to the designated API endpoint. For example, an image recognition API call would involve sending the image data as part of the request. Similarly, a natural language processing API call might require passing text as input.
The response from the API will contain the model’s output, which needs to be parsed according to the specified output format. Robust error handling is crucial to manage potential issues during API interactions.
Using Libraries for Interaction
Leveraging specialized libraries can significantly simplify the process of interacting with AI APIs. These libraries often provide convenient functions for constructing requests, handling responses, and managing potential errors. For example, Python libraries like `requests` facilitate the interaction with APIs, and specialized AI libraries provide tailored functions for tasks such as image recognition or natural language processing. These libraries handle the complexities of the API interaction, allowing developers to focus on the application logic.
Examples of API Interaction (Python)
“`pythonimport requestsdef make_image_recognition_call(image_data): “””Makes a call to an image recognition API.””” url = “https://api.example.com/image_recognition” headers = ‘Content-Type’: ‘image/jpeg’ # Example header response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=’image’: image_data) if response.status_code == 200: return response.json() # Parse the JSON response else: print(f”Error: response.status_code”) return None“`This Python code snippet demonstrates a basic function for interacting with an image recognition API.
It utilizes the `requests` library to send a POST request containing the image data. The response is parsed, and appropriate error handling is implemented.
Popular AI APIs and Functionalities
| API | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Google Cloud Vision API | Image labeling, object detection, optical character recognition (OCR). |
| Amazon Rekognition | Image and video analysis, facial recognition, object detection. |
| OpenAI API | Natural language processing, text generation, image generation, and more. |
| Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services | Comprehensive suite of AI APIs, including computer vision, language, speech, and more. |
| Hugging Face Transformers | Access to pre-trained language models for tasks like text classification, question answering, and summarization. |
This table provides a concise overview of several popular AI APIs and their capabilities. Each API serves a specific set of functionalities, and the choice of API depends on the particular needs of the application.
Troubleshooting API Issues
Successfully interacting with AI APIs hinges on understanding how to identify and resolve potential problems. This section will guide you through common pitfalls and effective strategies for debugging API calls, ensuring smooth and reliable communication with AI services.
Identifying Common API Errors
Effective troubleshooting begins with recognizing the nature of the error. AI APIs, like other software systems, return specific error codes and messages to pinpoint the source of the issue. These messages are crucial for understanding the nature of the problem. A thorough examination of these error messages allows for targeted solutions and efficient problem resolution.
Strategies for Debugging API Calls
Several strategies facilitate the debugging process. First, meticulously review the API request parameters to ensure they adhere to the API’s specifications. Pay close attention to data types, formats, and required fields. Secondly, validate the input data against expected formats and ranges. Thirdly, examine the response code and carefully review the response body for any error messages.
Finally, test the API call incrementally, isolating components of the request to pinpoint the problematic section.
Interpreting Error Messages
AI API error messages are designed to offer clear and concise explanations. Understanding the terminology within these messages is crucial. Error codes often provide insight into the nature of the problem. For example, a 400 Bad Request error usually indicates a problem with the request itself. A 500 Internal Server Error signifies a problem on the API server’s end.
Carefully scrutinize the message content to understand the specific issue and identify possible solutions.
Troubleshooting Specific AI API Requests
This section demonstrates a step-by-step approach to troubleshoot a specific AI API request. Assume a request to a natural language processing API for sentiment analysis. The request includes a text input and an expected response containing sentiment scores.
- Verify API Keys and Permissions: Ensure the API key is correctly configured and that the application has the necessary permissions to access the specified endpoint. Incorrect keys or insufficient privileges can lead to authentication errors.
- Validate Request Parameters: Confirm that the input text conforms to the API’s required format. Incorrect data types, missing fields, or exceeding character limits can lead to a ‘Bad Request’ error. Check the API documentation for the specific input format and constraints.
- Examine Response Codes and Messages: Carefully analyze the HTTP status code returned by the API. Codes like 400, 401, 404, or 500 indicate potential issues. Examine the response body for error messages that pinpoint the problem.
- Iterative Testing: Gradually refine the request by simplifying the input text or by checking individual parts of the request to isolate the source of the error.
- Review API Documentation: Consult the API’s documentation for any known issues or troubleshooting guides that might be relevant to the specific problem.
Potential API Errors and Solutions
| Error | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 400 Bad Request | Incorrect request format, missing parameters, invalid data type | Review API documentation for correct format and data types. Ensure all required parameters are present and have valid values. |
| 401 Unauthorized | Incorrect or missing API key | Verify the API key. Check the API key format and ensure that the key is correctly added to the request headers. |
| 404 Not Found | Invalid endpoint or resource | Double-check the API endpoint URL. Confirm the endpoint exists and is accessible. |
| 500 Internal Server Error | Temporary API server issues | Wait for the server to become available. Try the API request again later. Monitor the API status for any known outages or maintenance windows. |
| Rate Limiting | Exceeding the allowed request rate | Implement appropriate delays between requests. Use pagination or other strategies to handle large datasets. |
Practical Applications
AI APIs unlock a wealth of possibilities for developers, enabling the creation of innovative applications across diverse industries. By leveraging pre-built functionalities, developers can focus on the unique aspects of their projects, accelerating development cycles and delivering sophisticated solutions. This section explores practical applications of AI APIs, showcasing real-world use cases and providing detailed integration examples.
Building a Chatbot
A significant application of AI APIs involves the creation of sophisticated chatbots. These bots can be integrated into various platforms, from customer support systems to interactive educational tools. Utilizing natural language processing (NLP) APIs, developers can build chatbots capable of understanding and responding to user queries in a human-like manner. The chatbot can be trained on a specific dataset to understand context and provide relevant answers.
This process often involves fine-tuning the model for optimal performance and ensuring accurate responses. For example, a customer service chatbot can handle common inquiries, freeing up human agents to address more complex issues.
Creating an Image Generator
AI APIs facilitate the creation of realistic images from text descriptions. Image generation APIs use deep learning models to translate textual input into visual representations. This capability has far-reaching applications in various fields. Imagine generating marketing materials with customized visuals based on descriptions, or creating personalized artwork based on user input. Specific applications include generating images for social media campaigns or developing tools for graphic design.
The generated images can be further manipulated or customized to match specific needs.
Real-World Use Cases in Different Industries
AI APIs find applications across diverse industries, enhancing efficiency and innovation. In healthcare, AI APIs can assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and personalizing treatment plans. Finance institutions leverage AI APIs for fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer service automation. Retail companies employ AI APIs to personalize recommendations, optimize inventory management, and improve customer experience. This integration demonstrates how AI APIs can be customized to meet the specific needs of different industries.
Integrating AI APIs into Existing Applications
Integrating AI APIs into existing applications is a straightforward process. Developers can utilize API libraries and SDKs to seamlessly integrate the API into their applications. This process often involves making API calls from the application to access the AI service, receiving the response, and processing the results within the application’s logic. Detailed documentation provided by API providers often includes examples of how to perform API calls and handle responses.
A crucial aspect is error handling, enabling the application to gracefully manage unexpected situations.
Detailed Case Study: Image Recognition in E-commerce
A retail company, “FashionForward,” aims to enhance its e-commerce platform by implementing image recognition capabilities. The company uses an AI API for image tagging and categorization. By integrating this API into its product upload process, FashionForward allows customers to search for products based on visual attributes. This feature increases product discoverability, improves user experience, and facilitates targeted marketing campaigns.
The company collects user feedback to optimize the API’s performance and enhance the user experience. This detailed case study showcases the potential of AI APIs in transforming business operations.
Security Considerations
Ensuring the security of your interactions with AI APIs is paramount. Compromised credentials or vulnerabilities in the API can lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, or financial losses. Implementing robust security measures is crucial for maintaining data integrity and trust in AI-powered services.Protecting sensitive information, such as API keys and authentication tokens, is critical. Implementing secure storage and access controls are essential components of a comprehensive security strategy.
Furthermore, adhering to rate limits and throttling mechanisms prevents abuse and ensures fair access for all users.
API Key Management
Proper management of API keys is vital to prevent unauthorized access. Never hardcode API keys within your application code. Instead, store them securely in environment variables, configuration files, or dedicated secrets management services. These methods provide a layer of protection against accidental exposure or malicious code injection.
Credential Protection
Protecting API credentials, beyond API keys, is equally important. Employ strong password policies and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible. Regularly review and update credentials, especially when dealing with sensitive or high-value AI services. Consider using dedicated credential management tools to automate and streamline this process.
Rate Limiting and Request Throttling
Rate limiting and request throttling are essential security mechanisms. These techniques prevent overload attacks and ensure fair usage of the AI API. By enforcing limits on the number of requests per unit of time, you safeguard the API’s performance and prevent abuse. Properly configured rate limits protect the API from being overwhelmed by excessive requests, ensuring reliable service for all users.
Handling Potential Vulnerabilities
AI APIs, like any software, can be susceptible to security vulnerabilities. Regularly monitor for potential issues, such as injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS), or insecure direct object references. Implement appropriate input validation and output sanitization to mitigate these risks. Staying updated with the latest security advisories for the AI API you are using is crucial.
Security Measures for AI API Usage
| Security Measure | Importance |
|---|---|
| Secure Storage of API Keys | Prevents accidental exposure and unauthorized access. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra layer of security, requiring multiple forms of verification. |
| Regular Credential Review | Helps identify and address potential security weaknesses. |
| Rate Limiting/Request Throttling | Prevents abuse, ensures fair access, and protects API performance. |
| Input Validation/Output Sanitization | Reduces the risk of injection attacks and other vulnerabilities. |
| Regular Security Audits | Helps identify and address vulnerabilities proactively. |
Advanced Topics
Advanced API concepts are crucial for building robust and scalable AI systems. This section delves into more sophisticated aspects of API interaction, including versioning, caching, and gateway management, crucial for maintaining functionality and performance in evolving AI applications. Understanding API design principles and testing methodologies ensures the reliability and effectiveness of AI services.API gateways, versioning strategies, and robust testing procedures are essential for managing the complexities of AI systems.
Proper API design ensures the long-term maintainability and scalability of AI services.
API Versioning
API versioning is a critical practice for managing evolving AI systems. It allows developers to introduce new features and updates without breaking existing applications that rely on the API. This approach is particularly important in AI, where model improvements and new functionalities are frequent. Versioning ensures backward compatibility, facilitating smooth transitions and preventing disruptions in service usage.
For instance, a new version of an image recognition API might introduce a more accurate algorithm, but older clients can continue using the previous version without encountering problems. A common versioning scheme uses semantic versioning (e.g., 1.0.0, 1.1.0, 2.0.0), where the first number represents major changes, the second minor changes, and the third patch releases.
API Caching
Caching mechanisms are important for optimizing API performance. By storing frequently accessed data or results, APIs can significantly reduce latency and improve response times. In AI systems, especially those involving complex computations, caching can be invaluable. For example, if an AI model is frequently used to predict customer behavior, caching the results of past predictions can speed up subsequent requests.
This approach reduces the computational burden on the AI service and provides faster responses to client applications.
API Gateways
API gateways act as intermediaries between clients and backend services, providing crucial functionality for managing and controlling API traffic. They handle tasks such as authentication, authorization, rate limiting, and request transformation, thus enhancing security and efficiency. Use cases for API gateways in AI development include centralized authentication for different AI models, enforcing usage quotas to prevent abuse, and providing a unified entry point for various AI services.
API Documentation for AI Systems
Thorough documentation is essential for maintaining and evolving AI systems. Well-documented APIs make it easier for developers to integrate with and use the system. Comprehensive documentation should include clear explanations of each API endpoint, its parameters, expected responses, and potential error codes. This approach aids in troubleshooting and ensures consistency across different parts of the AI system.
This is especially important for complex AI models or when collaborating with other teams.
API Testing Methodologies and Tools
Testing methodologies and tools play a critical role in validating the accuracy and reliability of AI APIs. Testing strategies should cover various aspects of the API, including functionality, performance, security, and compatibility. This is crucial to ensure that the AI system performs as expected under different conditions and usage patterns. Specific testing methodologies might include unit testing of individual AI components, integration testing to ensure smooth interaction between different parts of the system, and performance testing to assess responsiveness under various loads.
Popular tools for API testing in AI development include Postman, REST Assured, and Swagger.
API Design Principles for AI Systems
API design principles are crucial for building scalable and maintainable AI systems. Key considerations include RESTful principles, using clear and descriptive names for endpoints and parameters, and ensuring proper error handling. Implementing these principles leads to better code organization and more predictable behavior, simplifying maintenance and future development. These principles ensure the quality and usability of the API, facilitating long-term development and scalability of AI services.
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, this guide has provided a detailed overview of how to understand and effectively utilize APIs for AI services. We’ve covered the essential elements, from understanding API documentation and concepts to practical applications and advanced topics. By mastering these techniques, you’ll be well-equipped to leverage the power of AI APIs and integrate them seamlessly into your projects, opening up a world of possibilities.