Artificial intelligence models are rapidly transforming various sectors, from healthcare to finance. Understanding these powerful tools is crucial for navigating the modern world. This guide provides a clear and accessible overview, demystifying the inner workings of AI models and their diverse applications.
This comprehensive exploration will cover everything from defining AI models and their fundamental components, to understanding the intricate process of data training and model evaluation. We will delve into the mathematical functions, various model architectures, and the real-world implications of AI.
Defining AI Models
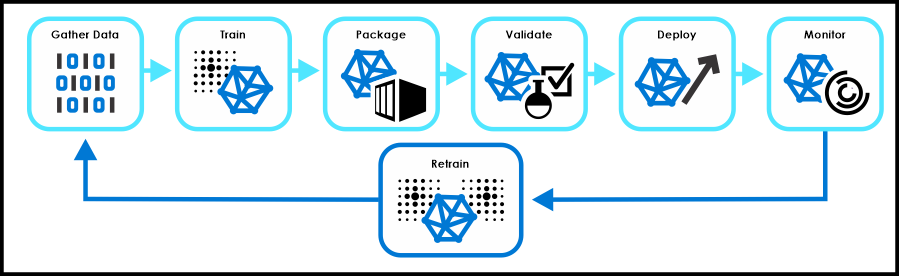
Artificial intelligence (AI) models are fundamental to various applications, from image recognition to personalized recommendations. They represent a set of rules and algorithms designed to learn from data and make predictions or decisions. Understanding their components and different types is crucial for grasping the capabilities and limitations of AI.AI models are essentially sophisticated programs that learn patterns and relationships within data.
They are trained on vast datasets to improve their accuracy and performance. The models’ ability to adapt and improve over time makes them powerful tools in various fields.
Core Components of an AI Model
AI models are built upon several key components. These include the input data, the model architecture, the learning algorithm, and the output. The input data provides the raw material for the model to learn from. The architecture defines the structure and connections within the model. The learning algorithm dictates how the model adjusts its internal parameters based on the data.
Finally, the output represents the model’s prediction or decision.
Types of AI Models
Different types of AI models employ various learning approaches. Understanding these approaches helps to appreciate the versatility of AI.
| Model Type | Description | Example | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | This type of model learns from labeled data, where each input example is paired with a corresponding output. The model learns to map inputs to outputs. | Predicting house prices based on features like size and location. | Requires labeled data, learns a mapping between input and output, often used for classification and regression tasks. |
| Unsupervised Learning | This type of model learns from unlabeled data, identifying patterns and structures without explicit guidance. | Customer segmentation based on purchasing behavior. | No labeled data required, discovers hidden patterns and structures in data, useful for clustering and dimensionality reduction. |
| Reinforcement Learning | This type of model learns through trial and error, interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties for its actions. | Training a robot to navigate a maze. | Learns through interaction with an environment, receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties, useful for tasks requiring sequential decision-making. |
Visual Representation of a Basic AI Model
Imagine a simplified AI model as a pipeline processing data. Data flows through the model, interacting with its components, and finally producing an output. The input data is processed through the model architecture. The learning algorithm adjusts the model’s parameters to optimize its performance. The output is the prediction or decision generated by the model.
[Visual representation of a simplified data flow diagram: Data (input) -> Model Architecture -> Learning Algorithm -> Output (prediction/decision)]
Understanding Model Structure

AI models, regardless of their complexity, rely on underlying mathematical functions and structured data processing. Understanding their internal workings is crucial to interpreting their outputs and evaluating their reliability. This section delves into the core components of model structure, illuminating the mathematical functions, data processing steps, and the roles of parameters and variables. Furthermore, it compares and contrasts various model architectures.
Mathematical Functions in AI Models
AI models employ a variety of mathematical functions to transform input data into meaningful outputs. These functions, often complex and interconnected, are crucial for tasks such as classification, regression, and clustering. For instance, in neural networks, activation functions introduce non-linearity, enabling the model to learn complex patterns. Examples include sigmoid, ReLU, and tanh functions. Linear transformations, using matrices and vectors, are also fundamental in manipulating input data.
f(x) = Wx + b, where W is a weight matrix, x is the input vector, and b is a bias vector, exemplifies a simple linear transformation.
Input Data Processing
Input data, regardless of its form (images, text, or numerical values), undergoes a series of transformations before it’s processed by the model. Data preprocessing is critical, often involving steps like cleaning, normalization, and feature engineering. Normalization, for example, ensures that features with larger values do not dominate the learning process. The format of the input data is adapted to fit the model’s requirements.
This might involve converting text into numerical representations, or images into pixel arrays. Subsequently, the data is fed into the model’s architecture.
Parameters and Variables in AI Models
Parameters and variables are essential elements in AI models. Parameters are internal model settings that are learned during the training process, optimizing the model’s performance on a given dataset. Variables, on the other hand, represent the input data points and intermediate results within the model’s calculations. The model adjusts the parameters to minimize errors and maximize accuracy in its predictions.
For instance, in a linear regression model, the slope and intercept are parameters, while the input data points are variables.
Comparison of AI Model Architectures
Different AI model architectures, like neural networks and decision trees, have distinct structures and functionalities. Neural networks, composed of interconnected nodes organized in layers, excel at learning complex patterns. In contrast, decision trees use a hierarchical structure of decisions to classify or predict outcomes. The choice of architecture depends on the nature of the problem and the characteristics of the available data.
Components of a Neural Network Model
Neural networks, a prevalent AI model type, are composed of interconnected nodes organized in layers. Understanding their structure is key to appreciating their power.
| Component | Description | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Layer | Receives the initial input data. | Passes the input data to the hidden layers. | Pixel values of an image |
| Hidden Layers | Process the input data using mathematical functions. | Extract features and patterns from the input data. | Identifying edges, shapes, and textures in an image. |
| Output Layer | Produces the final output of the model. | Generates the prediction or classification based on processed data. | Classifying an image as a cat or dog. |
| Weights | Numerical values that determine the strength of connections between nodes. | Control the influence of each input on the output. | 0.8, -0.5, 1.2 |
| Biases | Constants added to the weighted sum of inputs. | Shift the activation function’s output. | 0.3 |
| Activation Functions | Introduce non-linearity to the model. | Enable the model to learn complex patterns. | Sigmoid, ReLU, Tanh |
Data and Model Training
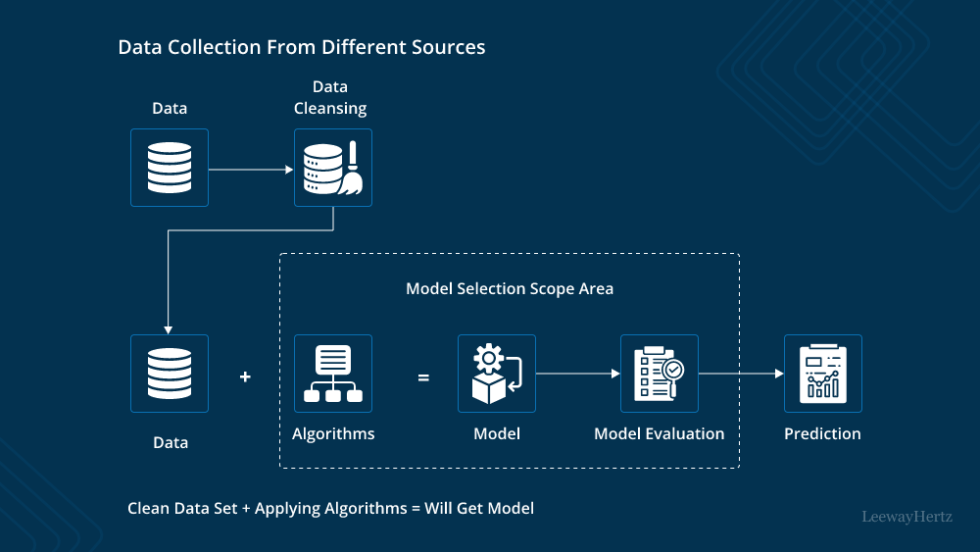
AI models are not magically created; they require careful training using vast amounts of data. This process shapes the model’s understanding and ultimately determines its performance. The quality and quantity of the training data significantly impact the model’s ability to learn and make accurate predictions. Furthermore, the algorithms employed during training dictate how the model extracts insights from the data, leading to different outcomes.
Data Used for Training
The foundation of any AI model lies in the data it’s trained on. This data represents real-world scenarios and characteristics that the model will learn to recognize and interpret. The type of data used varies significantly depending on the intended application. For instance, a model designed to identify images of cats will need a dataset containing numerous cat pictures.
Model Training Process
Model training involves feeding the model a large dataset of labeled examples. The model learns patterns and relationships within the data by adjusting its internal parameters. This iterative process continues until the model achieves a satisfactory level of performance. Crucially, a separate validation dataset is used to assess the model’s ability to generalize to unseen data. This crucial step prevents overfitting, where the model performs exceptionally well on the training data but poorly on new, unseen data.
Role of Algorithms
Algorithms are the set of rules and procedures that dictate how the model learns from the data. Different algorithms excel in different tasks and data types. For instance, linear regression is effective for predicting continuous values, while decision trees are suitable for classification problems. The choice of algorithm significantly influences the model’s learning process and, consequently, its accuracy.
Different Data Types
Various data types are used to train AI models. Images, representing visual information, are essential for tasks like object recognition and image classification. Text data, encompassing written content, fuels models for natural language processing, enabling tasks like sentiment analysis and language translation. Audio data, such as speech recordings, is vital for applications like speech recognition and music genre classification.
Each data type requires specialized techniques for preprocessing and feature extraction to be effectively utilized.
Effect of Training on Accuracy
Model training directly impacts model accuracy. The quality and quantity of the training data play a critical role. Insufficient data can lead to an underperforming model, while an excessive amount of irrelevant data can result in a model that overfits to the training data, leading to poor generalization. Properly designed algorithms, along with techniques like regularization, can mitigate these risks.
Moreover, careful tuning of the training parameters (such as learning rate and epochs) can further refine the model’s performance and achieve higher accuracy on unseen data. For example, a model trained on a comprehensive dataset of medical images for cancer detection is more likely to achieve higher accuracy than a model trained on a small, limited dataset.
Model Evaluation and Interpretation
Evaluating an AI model’s performance and understanding its reasoning is crucial for deploying it effectively. Proper evaluation helps determine if the model meets the desired accuracy and reliability standards. Interpreting the model’s output provides insight into its decision-making process, which is essential for building trust and ensuring responsible use.
Model Performance Evaluation Methods
Evaluating the performance of an AI model involves assessing its ability to accurately predict outcomes or classify data points. Various methods exist, each tailored to specific model types and applications. Common methods include using held-out datasets, cross-validation techniques, and metrics that measure different aspects of model accuracy.
Accuracy Assessment Metrics
Different metrics are used to quantify the accuracy of an AI model. Choosing the appropriate metric depends on the specific problem being addressed. Common metrics include precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the ROC curve (AUC). Precision measures the proportion of correctly predicted positive instances among all predicted positives, while recall measures the proportion of correctly predicted positive instances among all actual positives.
The F1-score balances precision and recall, providing a comprehensive measure of accuracy. The AUC is a measure of a model’s ability to distinguish between classes.
Model Output Interpretation Techniques
Understanding the reasoning behind a model’s predictions is crucial for building trust and ensuring its proper application. Techniques for interpreting model output include analyzing feature importance, visualizing decision boundaries, and using explainable AI (XAI) methods. Analyzing feature importance helps identify which input features most influence the model’s predictions. Visualizing decision boundaries helps understand how the model distinguishes between different classes or categories.
XAI methods provide human-readable explanations for the model’s decisions.
Example of Model Evaluation Results
| Metric | Value | Description | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.95 | Proportion of correctly classified instances | The model correctly classifies 95% of the instances. This suggests a high level of accuracy. |
| Precision | 0.90 | Proportion of correctly predicted positives among all predicted positives | Of all instances predicted as positive, 90% were actually positive. |
| Recall | 0.92 | Proportion of correctly predicted positives among all actual positives | The model correctly identified 92% of the actual positive instances. |
| F1-score | 0.91 | Harmonic mean of precision and recall | A balanced measure of precision and recall, indicating a high level of accuracy. |
| AUC | 0.98 | Area under the ROC curve | The model has a high ability to distinguish between positive and negative instances, indicating strong performance. |
Understanding Model Reasoning
Techniques for understanding the reasoning behind model predictions often involve examining the model’s internal workings. This can include inspecting feature importance scores, analyzing the decision path, or using visualization tools. Feature importance scores show which features contribute most to the model’s predictions. Analyzing the decision path reveals how the model arrives at a particular prediction. Visualization tools provide a graphical representation of the model’s decision boundaries.
Applications and Implications

AI models are transforming numerous fields, from healthcare to finance. Their ability to analyze vast datasets and identify patterns is leading to innovative solutions and advancements across various sectors. This section explores the diverse applications of AI models, their societal impact, and the crucial ethical considerations surrounding their use.Understanding the potential benefits and risks of AI models is essential for responsible development and deployment.
This includes recognizing their capabilities and limitations, as well as anticipating the societal changes they might bring.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
AI models are proving valuable tools in various industries. Their versatility allows for a wide range of applications, from automating tasks to providing insights for decision-making. The table below showcases the diverse applications of AI models in different sectors.
| Industry | Application | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Disease Diagnosis | AI models can analyze medical images (X-rays, MRIs) and patient data to assist in the early detection and diagnosis of diseases like cancer and other conditions. | Improved accuracy, faster diagnosis, reduced human error, and potential for personalized medicine. |
| Finance | Fraud Detection | AI models can identify patterns in financial transactions that may indicate fraudulent activity, helping financial institutions prevent losses. | Enhanced security, reduced financial losses, and improved efficiency in fraud prevention. |
| Retail | Personalized Recommendations | AI models analyze customer purchase history and preferences to provide tailored product recommendations, improving customer satisfaction and sales. | Increased customer engagement, improved sales, and better understanding of customer needs. |
| Manufacturing | Predictive Maintenance | AI models analyze machine sensor data to predict potential equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and preventing costly downtime. | Reduced maintenance costs, improved equipment lifespan, and increased operational efficiency. |
| Transportation | Autonomous Vehicles | AI models power self-driving cars, trucks, and other vehicles, promising safer and more efficient transportation systems. | Improved safety, reduced traffic congestion, and potential for increased accessibility. |
Societal Impacts of AI Models
AI models are rapidly changing various aspects of society. From automating tasks to providing personalized experiences, they are impacting employment, education, and social interactions. The extent of these impacts is still unfolding, and careful consideration of potential consequences is crucial.
Ethical Considerations in AI Model Development
Ethical considerations are paramount in the development and deployment of AI models. Bias in training data can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, and ensuring fairness and transparency is critical. Accountability and control mechanisms are also essential to mitigate potential harms.
Real-World Problem Solving with AI Models
AI models are already being used to address real-world problems in diverse sectors. For instance, AI-powered systems are helping to identify and monitor deforestation, contributing to conservation efforts. Another example involves the use of AI in agriculture, optimizing crop yields and resource use. These applications highlight the potential of AI models to improve human well-being and environmental sustainability.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, grasping the essence of AI models involves understanding their structure, the data they consume, and the methods used to evaluate their performance. This comprehensive guide has illuminated the multifaceted nature of AI models, from their fundamental building blocks to their real-world applications and ethical considerations. By exploring the complexities of AI models, we gain a deeper understanding of their transformative potential and the crucial role they play in shaping our future.